Graphene flexible OLED is the best solution of encapsulation OLED
Graphene flexible OLED is the best solution of encapsulation OLED
Graphene is the most strong material in the world and transparent also so that makes a lot of researchers and scientists target to compact graphene in many things for improving them.
One of this famous projects is a UK project led by Cambridge University researchers have set out in 2015 to develop such as this technology, and the researchers now report that they have demonstrated a viable graphene solution comparable to existing commercial OLED encapsulation technologies.
Additional to graphene strength graphene is the world’s most impermeable material also! the secret behind this super features comes from graphene is the thinnest material in the world so that can create many layers of tiny thickness that makes it ultra strong and impermeable!
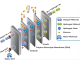
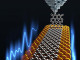
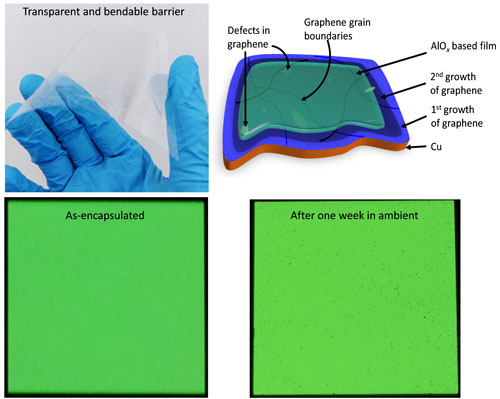
The new research used Atomic Layer Deposited (ALD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) to create large-area high-quality single-layer graphene sheets which were stacked to create a multi-layer coating. The researchers say that a ~10 nm barrier layer that includes 3-4 layers of graphene (with AlOx in between) is an effective solution for OLED displays. The 10 nm layer maintains a high optical transparency (>90 %) and high flexibility.
Importantly, this challenging task is accomplished by highly reliable measures of low water vapor transfer rates (WVTR) below 7×10-3 g / m2 per day, utilizing not only optical Ca tests and OLED life time determination, but also in the ppb level traceability facility at NPL
The team systematically benchmarked their results against the performance of existing state-of-the-art commercial multi-stacked barriers and industrially viable ALD aluminium oxide films and demonstrated that the nanolaminate films can be effectively integrated with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) enabling half-life times of 880 hours in ambient.
They also demonstrated the usability of their nanolaminates as a potential material to be included in standard multi-stacked barrier layers to enhance the performance of existing ALD aluminium oxide and produce next-generation moisture barriers.
This results highlight the potential of such heterogeneous substance integration and the use of such nanolaminates as a building block to engineer new functionalities and form factors for flexible and wearable technology.
The Source:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41699-017-0037-z