Graphene membranes used to produce heavy water and cleaning nuclear waste
Graphene membranes used to produce heavy water
Researchers at the University of Manchester a team led by Sir Andre Geim have demonstrated that graphene can simplify the production of heavy water and help clean nuclear waste by filtering different isotopes of hydrogen. The process could assist in producing heavy water for nuclear power plants with ten times less energy, making it simpler and cheaper.
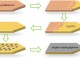
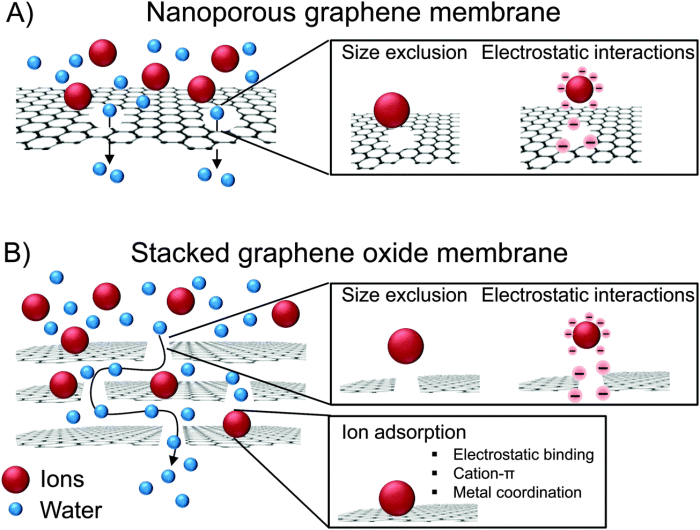
Membranes made from graphene can act as a sieve, separating protons – nuclei of hydrogen – from heavier nuclei of hydrogen isotope deuterium.
The process could mean producing heavy water for nuclear power plants could be ten times less energy intensive, simpler and cheaper using graphene. One of the hydrogen isotopes, Deuterium is in wide use in analytical and chemical tracing technologies and, also, as heavy water required in thousands of tons for the operation of nuclear power stations. The heaviest isotope, tritium, is radioactive and needs to be safely removed as a by-product of electricity generation at nuclear fission plants. Future nuclear technology is based on the fusion of the two heavy isotopes.
The researchers tested whether deuterons – nuclei of deuterium – can pass through graphene and boron nitride. They found that deuterons were not only effectively sieved out by the one atom thick membranes, but were sieved with high separation efficiency. The researchers referred to this as the first membrane shown to distinguish between subatomic particles, all at room temperature.
The researchers were surprised to find that deuterons were not only effectively sieved out by their one atom thick membranes, but were sieved with a high separation efficiency. The discovery makes monolayers of graphene and boron nitride attractive as separation membranes to enrich mixtures of deuterium and tritium. Furthermore, the researchers showed that the separation is fully scalable. Using chemical-vapor-deposited (CVD) graphene, they built centimetre-sized devices to effectively pump out hydrogen from a mixture of deuterium and hydrogen, the researchers showed that the separation is fully scalable. Using CVDrela graphene, they built centimeter-sized devices to effectively pump out hydrogen from a mixture of deuterium and hydrogen.
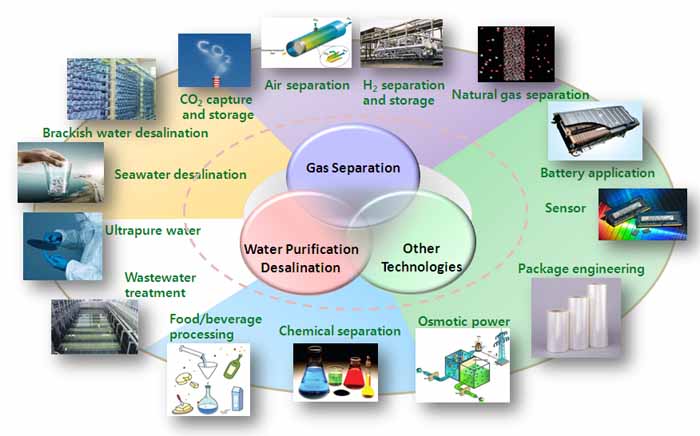
Graphene membranes have many uses in many fields also
Deuterium in nature:
In natural can found a massive amount of Deuterium but the problem filtered it Deuterium (symbol D or 2H, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. The nucleus of deuterium called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common hydrogen isotope, protium, has no neutron in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth’s oceans of about one atom in 6420 of hydrogen. Thus, deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% (or on a mass basis 0.0312%) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans while the most common isotope (hydrogen-1 or protium) accounts for more than 99.98%.